Understand
What are LLMs and How Do They Learn?
Overview
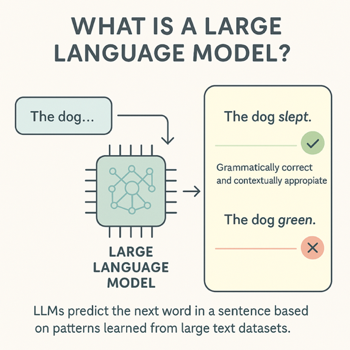
Large Language Models (LLMs) are a type of GenAI that learn patterns from vast amounts of text data. They are enormous in terms of both computing power and the amount of training data used.
The main job of an LLM is to predict which words are likely to appear next in a given phrase or sentence. At a basic level, this involves recognizing grammatical correctness, like preferring “the dog slept” over “the dog green.” However, modern LLMs consider larger contexts, helping them produce more accurate and nuanced responses.
Check Your Understanding
What else should I know?

